Counting Sort Sequential vs Parallel
Counting sort is an efficient algorithm for sorting an array of elements that each have a nonnegative integer key, for example, an array, sometimes called a list, of positive integers could have keys that are just the value of the integer as the key, or a list of words could have keys assigned to them by some scheme mapping the alphabet to integers (to sort in alphabetical order, for instance). Unlike other sorting algorithms, such as mergesort, counting sort is an integer sorting algorithm, not a comparison based algorithm.
The complexity of the algorithm is Theta(n).
*An algorithm that maps the following input/output pair is called a sorting algorithm: *
- Input: An array, A, of size of orderable elements.
A[0,1,...,n-1]. - Output: A sorted permutation of A, called B, such that
B[0]<=B[1]..<=B[n-1].
Counting Sort Sequential
Counting sort assumes that each of the n input elements in a list has a key value ranging from 0 to k, for some integer k. For each element in the list, counting sort determines the number of elements that are less than it. Counting sort can use this information to place the element directly into the correct slot of the output array.
Counting sort uses three lists:
-
A[0,1, ...,n]the input list. -
B[0,1, ...,n]the output list. -
C[0,1, ...,k]an temporany memory array.
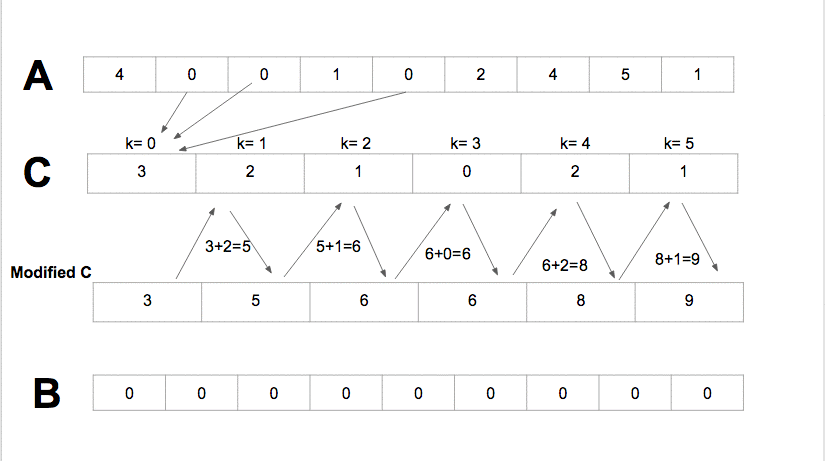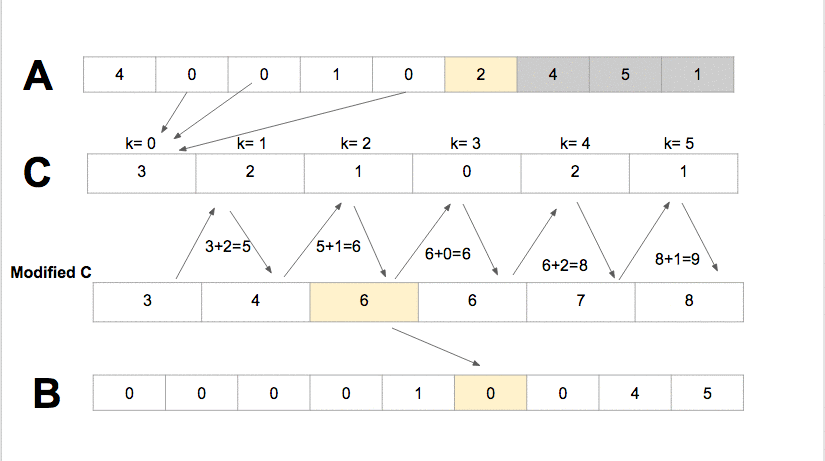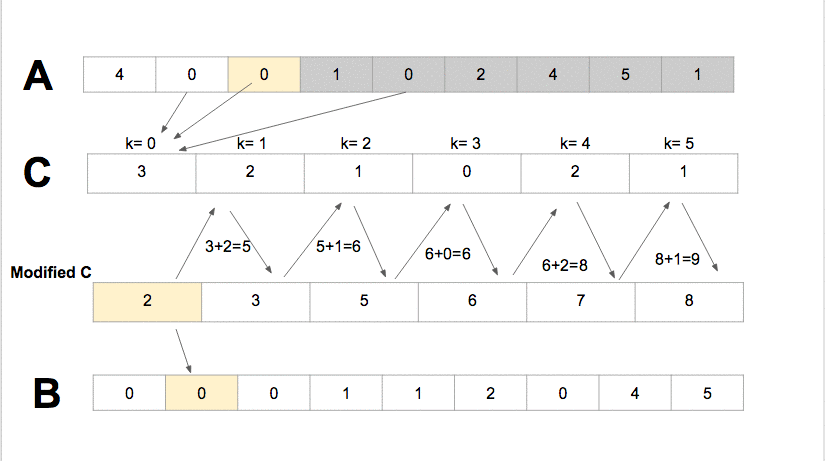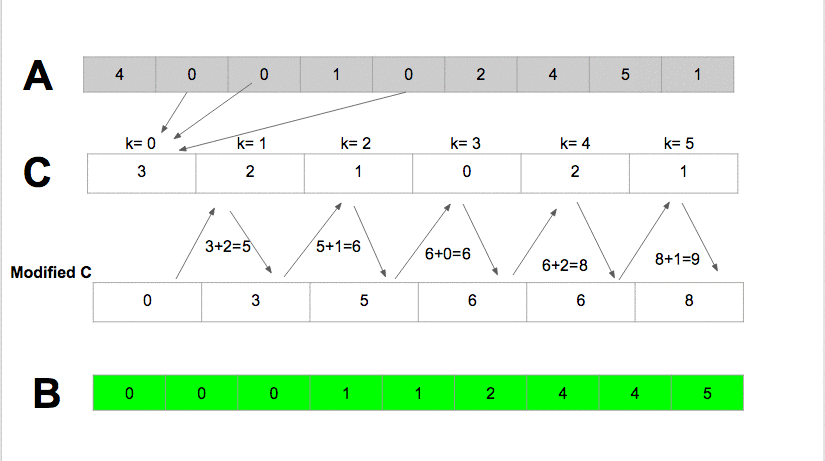
Algorithm
- Compute the min and the max of the arrat A in order to define
k= max - min + 1. - For all element in
A[i],0<=i<=n-1, the counting sort, incremente the valueC[A[i]-min]by one. For instance consider that the value 1 in the array A appears 8 times the valueC[1]=8. - Update the status of C with
C[i]=C[i]+C[i-1], 1<=i<=k. - Sort A in B according to
C[A[i]], 1<=i<=kand decrement the value ofC[A[i]]after each update.
Counting Sort Parallel
Bsed on the idea of sequential counting sort. Uses n^2 processors on a mesh grid of n x n. Running time complexity O(logn).

Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: